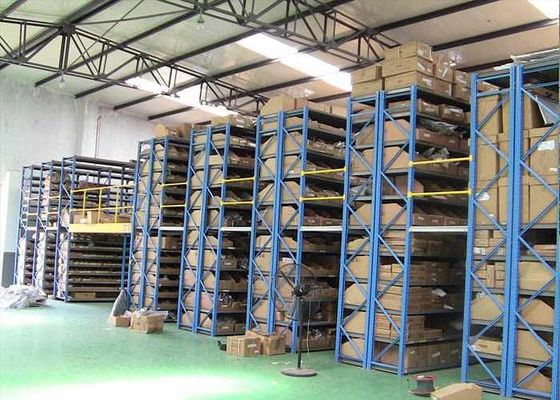
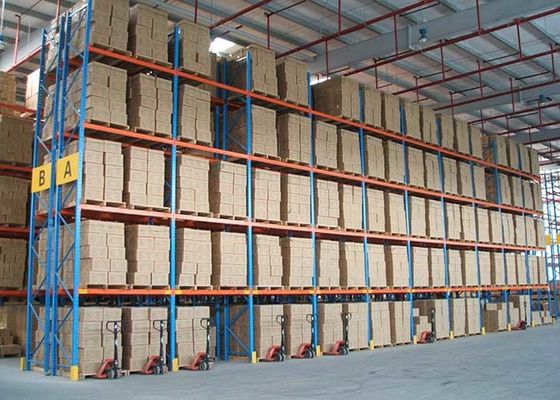
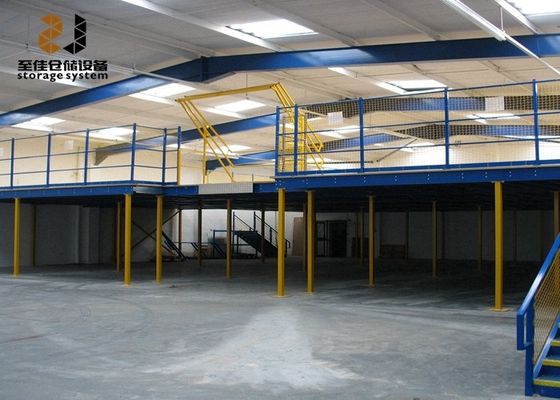
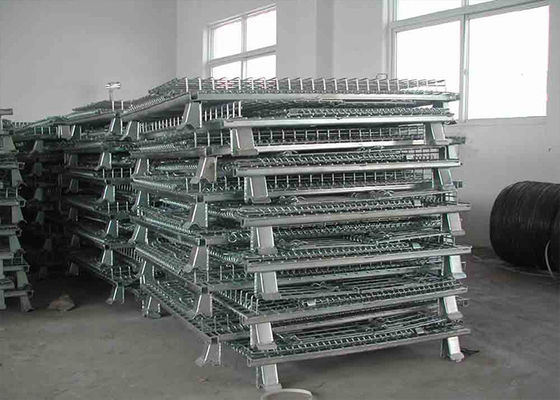
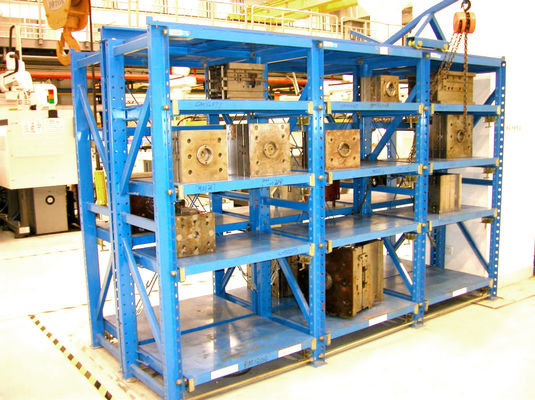
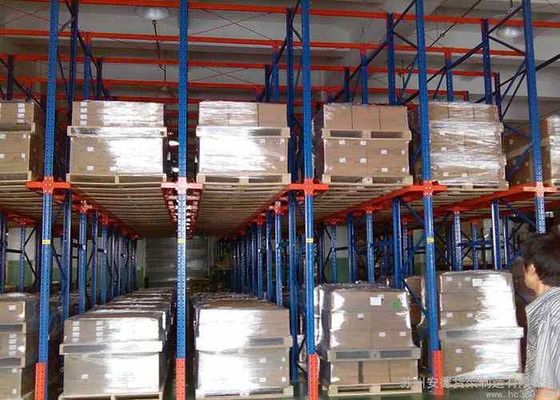
Le choix d'étagères de stockage industrielles en acier de haute qualité est essentiel pour garantir la sécurité opérationnelle, maximiser l'utilisation de l'espace de l'entrepôt et prolonger la durée de vie des équipements. Le processus de sélection doit être systématique, en se concentrant sur les exigences de charge, la stabilité structurelle, la qualité des matériaux et la compatibilité avec les scénarios d'application réels. Voici un guide détaillé, étape par étape, pour vous aider à faire un choix éclairé :
Avant de sélectionner une étagère, définissez clairement vos scénarios d'utilisation et vos besoins—c'est la base d'une sélection précise. Les facteurs clés à confirmer incluent :
- Capacité de charge: Calculez le poids d'un seul article stocké (par exemple, 50 kg/unité, 500 kg/unité) et la charge totale par niveau (poids d'un seul article × quantité par niveau). Les étagères sont classées par charge :
- Légère : ≤150 kg/niveau (pour les petites pièces, les composants électroniques).
- Moyenne : 150–500 kg/niveau (pour les cartons, les petites pièces de machines).
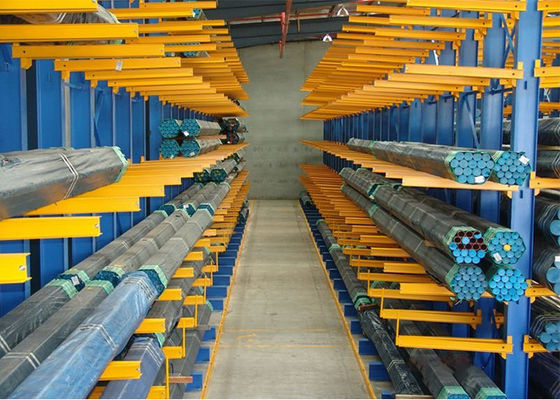
- Forte : ≥500 kg/niveau (pour les matériaux métalliques, les gros équipements, les palettes).
Remarque : Ne dépassez jamais la charge nominale de l'étagère—la surcharge est la principale cause de déformation ou d'effondrement structurel.
- Caractéristiques des articles stockés:
- Dimensions (longueur, largeur, hauteur) : Déterminez la hauteur du niveau de l'étagère, la longueur des traverses et la profondeur (par exemple, pour les palettes de 1,2 m de long, choisissez des traverses ≥1,2 m).
- Forme (encombrante, irrégulière ou petite) : Les articles encombrants peuvent nécessiter des traverses renforcées ; les petites pièces peuvent avoir besoin d'accessoires assortis comme des planchers grillagés ou des séparateurs.
- Méthode de stockage (prélèvement manuel, accès par chariot élévateur, robot AGV) : Les étagères accessibles par chariot élévateur nécessitent une résistance structurelle et une conception anti-collision plus élevées ; les étagères compatibles AGV nécessitent un étalonnage dimensionnel précis.
- Contraintes d'espace de l'entrepôt:
- Hauteur du sol : Déterminez le nombre de niveaux d'étagères (par exemple, une hauteur de sol de 5 m peut accueillir 3–4 niveaux d'étagères robustes).
- Capacité de charge du sol : Confirmez si le sol de l'entrepôt peut supporter le poids total de l'étagère (les étagères robustes nécessitent souvent un renforcement du sol ou des fondations en béton).
- Largeur des allées : Adaptez l'équipement de manutention (par exemple, des allées de 3–4 m pour les chariots élévateurs standard, 1,5–2 m pour les chariots élévateurs à allées étroites).
Les étagères industrielles en acier reposent entièrement sur les performances des matériaux pour la capacité de charge et la durabilité. Concentrez-vous sur les indicateurs suivants :
- Qualité de l'acier:
- Les étagères de haute qualité utilisent de l'acier à haute résistance et à faible alliage Q235B ou Q355B (norme nationale GB/T 700). Le Q355B a une résistance à la traction (≥345 MPa) et une résistance aux chocs plus élevées que le Q235B, ce qui le rend adapté aux scénarios à usage intensif.
- Évitez l'acier de qualité inférieure (par exemple, Q195) ou l'acier recyclé—ces matériaux sont sujets à la rouille, à la déformation et à la fracture sous charge.
- Épaisseur des composants clés:
- Vérifiez l'épaisseur des montants (colonnes verticales), des traverses (parties horizontales de support de charge) et des entretoises. Par exemple :
- Étagères légères : Montants ≥1,5 mm, traverses ≥1,2 mm.
- Étagères robustes : Montants ≥2,5 mm, traverses ≥3,0 mm.
Conseil : Utilisez un pied à coulisse pour mesurer l'épaisseur réelle—certains fabricants peuvent « couper les coins ronds » en réduisant l'épaisseur pour réduire les coûts.
- Procédé de traitement de surface:
- Le revêtement de surface affecte directement la résistance à la rouille et la durée de vie. La priorité est donnée à :
- Revêtement en poudre électrostatique: Après phosphatation (élimination de la rouille), pulvérisation électrostatique de poudre époxy-polyester et cuisson à haute température (180–200°C). Caractéristiques : Revêtement uniforme (épaisseur de 60–80μm), forte adhérence, résistance aux rayures et respect de l'environnement (pas de métaux lourds).
- Galvanisation à chaud: Convient aux environnements extérieurs ou humides (par exemple, entrepôts frigorifiques, entrepôts de produits chimiques). La couche de zinc (≥85μm) offre une excellente résistance à la corrosion, mais est plus chère.
- Évitez les étagères avec peinture au pistolet (revêtement fin, facile à décoller) ou galvanoplastie (mauvaise adhérence, métaux lourds toxiques).
Une conception structurelle raisonnable peut répartir la charge uniformément et réduire le risque d'effondrement. Points de contrôle clés :
- Structure des montants:
- Les montants de haute qualité utilisent des profilés à froid à double colonne ou en forme de C (pas de pliage d'une seule feuille), qui ont une plus grande résistance à la pression latérale (empêche l'inclinaison lors du chargement).
- Vérifiez si les montants ont des nervures de renfort (aux joints ou aux sections intermédiaires)—cela améliore la résistance à la flexion.
- Connexion traverse-montant:
- La connexion la plus sûre est la structure à emboîtement + fixation par boulons (pas seulement à emboîtement). La conception à emboîtement assure une installation rapide, tandis que les boulons empêchent la traverse de se détacher en raison des vibrations (par exemple, l'impact d'un chariot élévateur).
- Évitez les étagères avec uniquement des connexions soudées—les soudures sont sujettes aux fissures sous charge répétée, et la soudure rend le démontage/la modification impossible.
- Accessoires de support de niveau:
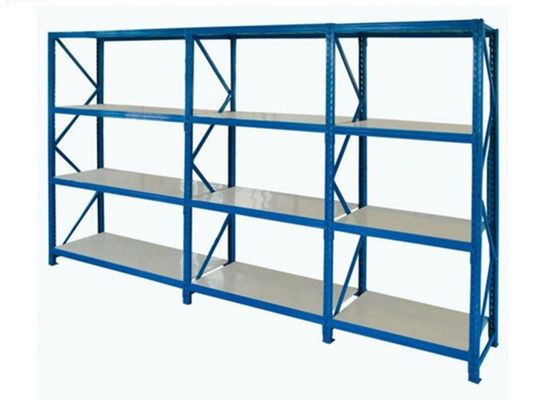
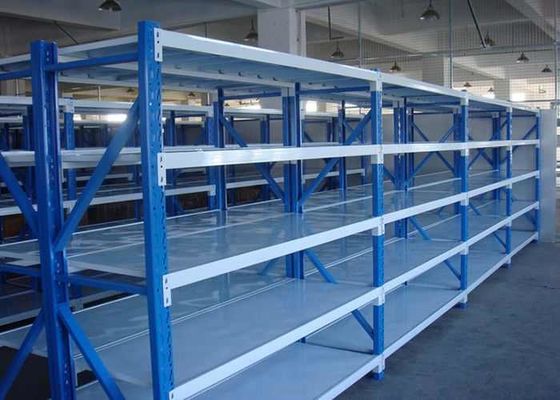
- Choisissez le platelage approprié en fonction des articles stockés :
- Palettes : Utilisez des supports de palettes en acier (en forme de L ou de U) pour fixer les palettes et éviter qu'elles ne glissent.
- Cartons/petites pièces : Utilisez des planchers grillagés (ventilés, faciles à nettoyer) ou des planchers en tôle d'acier (capacité de charge élevée).
- Pour les étagères robustes, ajoutez des diagonales (entre les montants) ou des tiges d'attache horizontales (entre les niveaux) pour améliorer la stabilité globale (résiste aux forces latérales des chariots élévateurs).
- Protection anti-collision:
- Les étagères dans les zones accessibles aux chariots élévateurs doivent être équipées de protecteurs de base (manchons en caoutchouc ou en acier au bas des montants) et de protections de colonnes (plaques d'acier enroulées autour des montants) pour réduire les dommages causés par les collisions accidentelles.
Les étagères industrielles formelles doivent répondre aux normes de sécurité nationales/internationales. Privilégiez les produits avec les certifications suivantes :
- Normes nationales: Conformez-vous à la norme GB/T 27924-2011 Exigences techniques pour les étagères de stockage industrielles (spécifie les indicateurs de capacité de charge, de matériaux et de sécurité).
- Certifications internationales: Pour les entrepôts d'exportation ou de haut niveau, recherchez les certifications CE (UE), RMI (ANSI MH16.1, norme de sécurité des étagères aux États-Unis) ou ISO 9001 (certification du système de gestion de la qualité).
- Rapports d'essais: Demandez au fabricant des rapports d'essais de charge statique (vérifiez si l'étagère peut supporter la charge nominale sans déformation pendant 24 heures) et des rapports d'essais d'impact (simulez l'impact d'un chariot élévateur pour vérifier l'intégrité structurelle).
Avertissement : N'achetez pas de produits « sans trois » (pas de marque, pas de normes, pas de rapports d'essais)—ils n'offrent aucune garantie de sécurité.
Les besoins des entrepôts sont souvent personnalisés, de sorte que les capacités de personnalisation et le support après-vente sont essentiels pour une utilisation à long terme :
- Capacités de personnalisation:
- Vérifiez si le fabricant peut ajuster les dimensions de l'étagère (hauteur, largeur, profondeur), la capacité de charge et les accessoires en fonction de vos besoins (par exemple, ajouter des cloisons pour les petites pièces, concevoir des étagères multicouches pour les hauts plafonds).
-
| Personne à contacter : |
Ms. vivian |
| Téléphone : |
+86 0769-83726626 |

 Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères!
Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères! Merci de consulter vos emails!
Merci de consulter vos emails!  Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères!
Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères! Merci de consulter vos emails!
Merci de consulter vos emails!